First Object 3D Printed in Space

The first object ever printed in space is this replacement part for the extruder head. Courtesy of Made In Space.
Latest News
November 26, 2014
How cool is a technology if NASA wants to test it out on the International Space Station (ISS)? Additive manufacturing (AM) may well be one of the vital keys to future manned and unmanned space exploration. The power to create new tools, spare parts and even food from base components would make AM systems one of the most flexible tools possible for exploration.
Made In Space is the company responsible for the printer currently onboard the ISS, and Rapid Ready has been following the company’s progress. The Made in Space 3D printer is basically a Fused Deposition Modeling-type system, with plastic as its primary material. 3D designs and instructions are provided by a laptop.
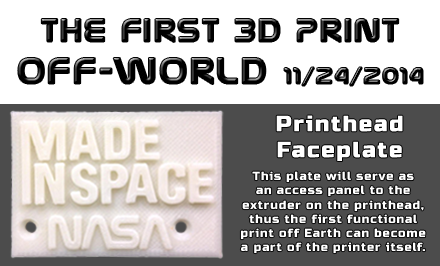 The first object ever printed in space is this replacement part for the extruder head panel. Courtesy of Made In Space.
The first object ever printed in space is this replacement part for the extruder head panel. Courtesy of Made In Space.“This first print is the initial step toward providing an on-demand machine shop capability away from Earth,” said Niki Werkheiser, project manager for the International Space Station 3-D Printer at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL. “The space station is the only laboratory where we can fully test this technology in space.”
The first object printed in space was a replacement faceplate for the extruder, bearing the logos of both NASA and Made in Space. Early reports indicate that the new part stuck to the build plate more strongly than had been anticipated, which may indicate a difference in how layers bond when without gravity. If the lack of gravity does make the bonds stronger, that may well prove to be an unforeseen bonus, resulting in more durable prints.
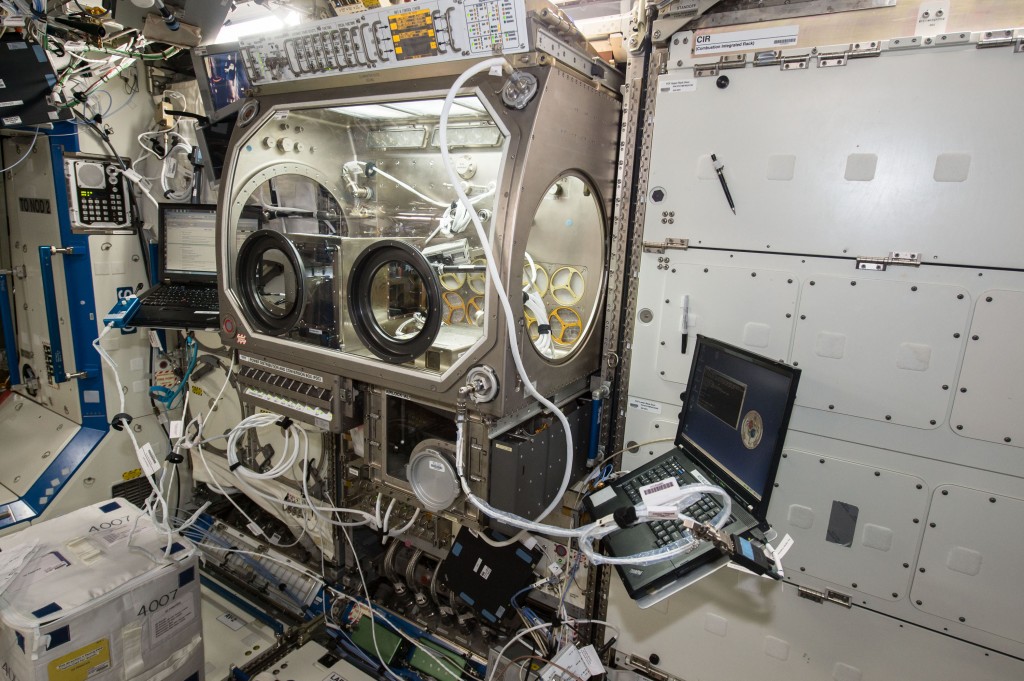 The Made In Space printer at rest in the Microgravity Science Glovebox. Courtesy of Made In Space.
The Made In Space printer at rest in the Microgravity Science Glovebox. Courtesy of Made In Space.Parts built in space will be returned to the Earth to undergo additional testing to see what, if any, changes need to be made to the system, and how 3D printing fares in space. Assuming all goes well, AM is likely to become an integral part of nearly every space mission from this point forward.
“The operation of the 3D printer is a transformative moment in space development,” said Aaron Kemmer, CEO of Made In Space. “We’ve built a machine that will provide us with research data needed to develop future 3D printers for the International Space Station and beyond, revolutionizing space manufacturing. This may change how we approach getting replacement tools and parts to the space station crew, allowing them to be less reliant on supply missions from Earth.”
Below you’ll find a video about Made in Space.
Sources: Made In Space, NASA
Subscribe to our FREE magazine, FREE email newsletters or both!
Latest News
About the Author
John NewmanJohn Newman is a Digital Engineering contributor who focuses on 3D printing. Contact him via [email protected] and read his posts on Rapid Ready Technology.
Follow DE