NVIDIA Launches UK-based Supercomputer for Research
AI supercomputers to enable UK researchers in digital biology, genomics, quantum computing and AI.

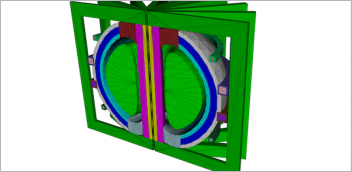
Cambridge-1, the United Kingdom’s supercomputer, will enable top scientists and healthcare experts to use a combination of artificial intelligence and simulation for future medical technological innovations. Image courtesy of NVIDIA.
Latest News
July 12, 2021
NVIDIA has launched Cambridge-1, the United Kingdom’s supercomputer, which will enable top scientists and healthcare experts to use the combination of artificial intelligence and simulation to accelerate digital biology technology and bolster the country’s life sciences industry.
Dedicated to advancing healthcare, Cambridge-1 represents a $100 million investment by NVIDIA. Its first projects with AstraZeneca, GSK, Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, King’s College London and Oxford Nanopore Technologies include developing a deeper understanding of brain diseases like dementia, using AI to design new drugs and improving the accuracy of finding disease-causing variations in human genomes.
Cambridge-1 brings together decades of NVIDIA’s work in accelerated computing, AI and life sciences, where NVIDIA Clara and AI frameworks are optimized to take advantage of the entire system for large-scale research. An NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD supercomputing cluster, it ranks among the world’s top 50 fastest computers and is powered by 100% renewable energy.
“Cambridge-1 will empower world-leading researchers in business and academia with the ability to perform their life’s work on the U.K.’s most powerful supercomputer, unlocking clues to disease and treatments at a scale and speed previously impossible in the U.K.,” says Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of NVIDIA. “The discoveries developed on Cambridge-1 will take shape in the U.K., but the impact will be global, driving groundbreaking research that has the potential to benefit millions around the world.”
Cambridge-1 builds on the U.K.’s status in life sciences, technology and AI by providing advanced infrastructure for current and future generations to carry out research within the country.
An economics consulting firm, according to a report by Frontier Economics, Cambridge-1 has the potential to create an estimated value of £600 million (about $825 million) over the next 10 years.
Drug Discovery with AI
NVIDIA is collaborating with AstraZeneca to fuel faster drug discoveries by creating a transformer-based generative AI model for chemical structures. Transformer-based neural network architectures, which have become available only in the last several years, allow researchers to leverage massive datasets using self-supervised training methods, avoiding the need for manually labeled examples during pre-training.
The MegaMolBART drug discovery model is being used in reaction prediction, molecular optimization and de novo molecular generation and will optimize the drug development process. It is based on AstraZeneca’s MolBART transformer model and is being trained on the ZINC chemical compound database—using NVIDIA’s Megatron framework to enable massively scaled-out training on supercomputing infrastructure. This open-source model will be available to researchers and developers in the NVIDIA NGC software catalog.
Steering Great Science with Partners for Patients
GSK’s research and development approach includes a focus on genetically validated targets, which are twice as likely to become medicines and now make up more than 70% of its research pipeline. To maximize the potential of these insights, GSK has built state-of-the-art capabilities at the intersection of human genetics, functional genomics, and artificial intelligence and machine learning.
“Advanced technologies are core to GSK’s R&D approach and help to unlock the potential of large, complex data through predictive modeling at new levels of speed, precision and scale,” says Dr. Kim Branson, senior vice president and global head of AI-ML at GSK. “We are pleased to have the opportunity to partner with NVIDIA to deliver on GSK’s drug discovery ambition and contribute to the U.K.’s rich life sciences ecosystem — both aims that have patient benefit at the centre.”
AI-Generated Synthetic Brain Data
King’s College London and Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust are using Cambridge-1 to teach AI models to generate synthetic brain images by learning from tens of thousands of MRI brain scans, from various ages and diseases. The ultimate goal is to use this synthetic data model to gain a better understanding of diseases like dementia, stroke, brain cancer and multiple sclerosis and enable earlier diagnosis and treatment.
As this AI synthetic brain model can generate an infinite amount of never-seen brain images with chosen characteristics (age, disease, etc.), it will allow a better and more nuanced understanding of what diseases look like, possibly enabling an earlier and more accurate diagnosis.
“Through this partnership, we will be able to use a scale of computational power that is unprecedented in healthcare research,” says Professor Sebastien Ourselin, head of the School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences at King’s College London. “It will be truly transformational for the health and treatment of patients.”
Scalable, Real-Time Genomics
Oxford Nanopore Technologies’ sequencing technology is being used in more than 100 countries to gain genomic insights across a breadth of research areas—from human and plant health to environmental monitoring and antimicrobial resistance.
Oxford Nanopore deploys NVIDIA technology in a variety of genomic sequencing platforms to develop AI tools that improve the speed and accuracy of genomic analysis. With access to Cambridge-1, Oxford Nanopore will be able to carry out tasks relating to algorithm improvement in hours rather than days. These improved algorithms will ensure improved genomic accuracy for greater insights and quicker turnaround times in scientists’ hands.
About Cambridge-1
Cambridge-1 is a NVIDIA supercomputer designed and built for external research access. The company will collaborate with researchers to make much of this work available to the greater scientific community.
Featuring 80 DGX A100 systems integrating NVIDIA A100 GPUs, BlueField-2 DPUs and NVIDIA HDR InfiniBand networking, Cambridge-1 is an NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD that delivers more than 400 petaflops of AI performance and eight petaflops of Linpack performance. The system is located at a facility operated by NVIDIA partner Kao Data.
Cambridge-1 is a supercomputer NVIDIA has dedicated to advancing industry-specific research in the U.K. The company also intends to build an AI Center for Excellence in Cambridge featuring a new Arm-based supercomputer, which will support more industries across the country.
Learn more about the Cambridge-1 supercomputer.
Sources: Press materials received from the company and additional information gleaned from the company’s website.
More NVIDIA Coverage
Subscribe to our FREE magazine, FREE email newsletters or both!
Latest News
About the Author
DE’s editors contribute news and new product announcements to Digital Engineering.
Press releases may be sent to them via [email protected].