Dassault Systèmes Announces New Release of Abaqus FEA from SIMULIA
Features improved realistic simulation capabilities.
Latest News
November 24, 2009
By DE Editors
Dassault Systemes has announced the availability of Abaqus 6.9 Extended Functionality (6.9-EF), its unified finite element analysis (FEA) product suite from SIMULIA.
 The improved implicit dynamics procedure in Abaqus 6.9-EF effectively solves challenging contact problems such as this gear pawl mechanism. |
This latest release delivers new features and enhancements for modeling, advanced mechanics, and performance. These ongoing improvements are enabling customers to consolidate their simulation software, which may help to lower cost and increase efficiency.
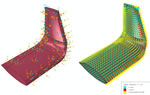 Using the new Discrete Orientation option in Abaqus, you can define spatially varying material orientation or orientation for composite layups on curved parts such as an aircraft winglet component. The image shows the orientation defined during preprocessing and as applied on the mesh and visualized during postprocessing. |
New features and enhancements in Abaqus 6.9-EF release include:
Modeling
- Interactive support is provided for meshing models using cylindrical elements, which can be useful in the analysis of pipelines by oil and gas companies.
- Geometry repair tools in Abaqus/CAE offer greater flexibility and broader scope for systematically adjusting the geometry of a model in preparation for meshing.
- An interface for model change definitions allows the deactivation and reactivation of model regions and contact pairs during an analysis.
- Users can now define direct cyclic and low-cycle fatigue analysis procedures in Abaqus/CAE. Low-cycle fatigue analysis can be used to efficiently predict fatigue life in electronic components such as solder joints.
- Discrete orientations provide a convenient method for defining spatially varying material orientations on models with curved geometries, such as aircraft panels and car bodies.
Advanced Mechanics
- Viscoelastic behavior can be now modeled with orthotropic/anisotropic elasticity in Abaqus/Explicit, which provides more realistic composite damage prediction.
- A new and efficient method is available for analyzing structures subject to air blast loading, which is useful for safety evaluation in the civil engineering and defense industries.
- Continued advancements in fracture and failure include contour integral evaluation for cracks defined with XFEM and the inclusion of the Virtual Crack Closure Technique (VCCT) in Abaqus/Explicit, which allows users to model brittle fracture of partially bonded surfaces.
- Breakthrough improvement in the implicit dynamics procedure helps solve unstable problems involving contact, buckling, and material failure. Examples include impact inside gear mechanisms and medical device deployment within patients.
Performance
- A new iterative solver in Abaqus/Standard provides performance gains up to 20x or more in comparison to the direct sparse solver, according to the company. The iterative solver is intended for very large simulation problems typically found in applications such as powertrain, oil reservoir, and material microstructure simulations.
- Performance when creating high-quality surface meshes using the mapped meshing technique has been significantly improved.
For more information, visit SIMULIA.
Go directly to the Abaqus FEA webpage.
Learn more about Abaqus/Standard.
Learn more about Abaqus/Explicit.
See why DE’s Editors selected Abaqus FEA selected as their Pick of the Week.
Subscribe to our FREE magazine, FREE email newsletters or both!
Latest News
About the Author
DE’s editors contribute news and new product announcements to Digital Engineering.
Press releases may be sent to them via [email protected].